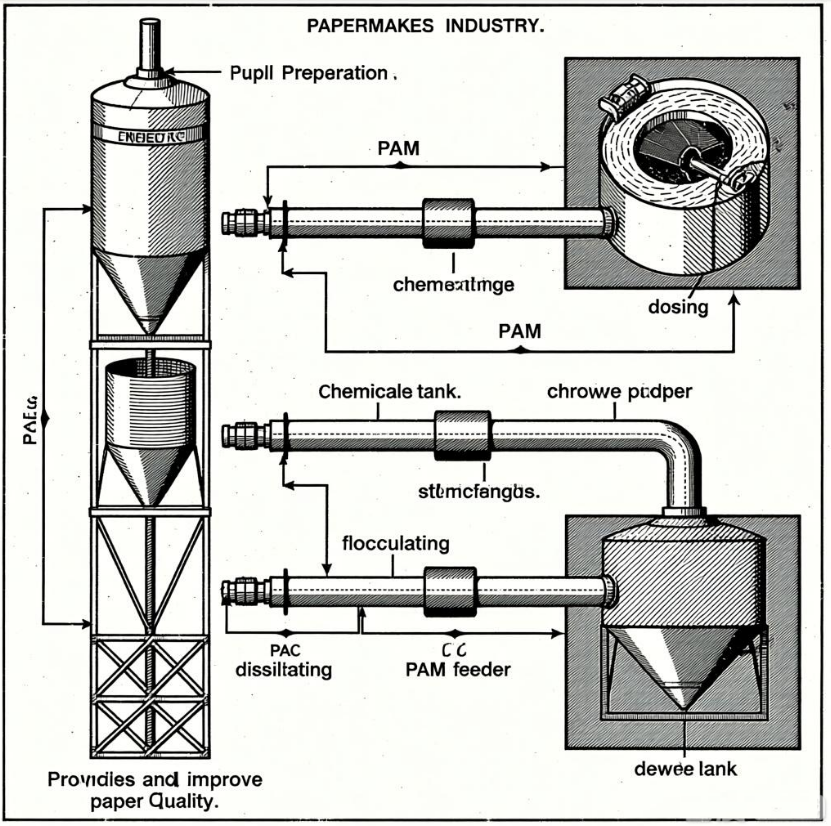
PAC (polyaluminum chloride) and PAM (polyacrylamide) in the papermaking industry
In general, they are indispensable chemical additives in the papermaking process, mainly used in two major areas: "papermaking wet-end chemistry" and "wastewater treatment." They often work synergistically to achieve optimal results.
Main uses of PAC (polyaluminum chloride):
As a strongly cationic inorganic polymeric coagulant, PAC's core function is "charge neutralization."
1. In the papermaking wet-end (production process):
(1)As a precursor in binary retention systems: This is the most advanced application of PAC in modern papermaking. It is added to the pulp before PAM to neutralize the negative surface charge of fibers, fillers, and other substances, destabilizing fine particles and laying a solid foundation for the subsequent bridging effect of PAM.
(2)Controlling "anionic waste": Papermaking raw materials (especially recycled pulp) contain a large amount of dissolved anionic organic matter (such as lignin and hemicellulose), which can interfere with the effectiveness of other chemicals. PAC can effectively neutralize these substances, stabilizing the chemical environment of the entire production system. 1. Improved filtration performance: By forming denser flocs, it accelerates the dewatering speed of the pulp on the wire, thereby increasing paper machine speed and output.
2. In wastewater treatment:
As a coagulant: Used to treat combined wastewater from paper mills. It effectively removes colloidal suspended solids, color, and some COD from the wastewater, clarifying the water and creating conditions for subsequent treatment or achieving discharge standards.
Main uses of PAM (polyacrylamide, mainly cationic CPAM):
As an organic polymer, PAM's core function is "adsorption bridging."
1. In the papermaking wet end (production process):
(1)As a highly efficient retention aid: This is PAM's primary function. Its long molecular chains act like "bridges," capturing and connecting fine fibers and fillers pretreated with PAC into large flocs, significantly improving their retention rate in the paper sheet.
Benefits: Saves raw material costs, increases the ash content (filler content) of the finished paper, and reduces the load on the white water system.
(2)As an excellent filter aid: By forming larger flocs, it alters the paper structure, creating more drainage channels and thus significantly accelerating pulp dewatering.
Benefits: Increases paper machine speed, reduces steam consumption in the drying section, and improves the uniformity of moisture distribution in the finished paper.
(3)As a reinforcing agent (minor role): By improving interfiber bonding, it has a certain effect on enhancing some physical strengths of the paper (such as dry strength).
2. In wastewater treatment:
As a flocculant: Usually added after PAC. PAC coagulates tiny colloidal particles into micro-flocculations, while PAM rapidly "captures" and "packages" these micro-flocculations into large, dense flocs that are visible to the naked eye.
Benefits: Significantly accelerates sedimentation/flotation speed, improves sludge dewatering efficiency, and increases the dryness of the sludge cake.
Core Collaborative Workflow (Very Important)
Their optimal efficiency lies in their collaborative operation, especially in binary polymer retention systems:
Step 1 (PAC): Add PAC at the high-shear point of the slurry delivery system (e.g., before the slurry pump).
Task: To neutralize the charge, "set the tone" of the system, and create a charge-stable environment.
Step 2 (PAM): Add CPAM at the low-shear point near the pre-screen box (e.g., after the pressure screen).
Task: In a stable charge environment, it acts as an "adsorption bridge," forming flocs of ideal size and strength, thereby achieving efficient retention and filtration.
PAC is like an "icebreaker," allowing all negatively charged particles to approach each other without repulsion.
PAM is like an "organizer," organizing these already close-approaching particles into a tight-knit team (large floc).